Real talk: hope is not a strategy! Your marketing campaigns have to add up to revenue. As an economist-turned-marketer, I take solace in quantifying problems and working from tangible plans. Enter the demand gen model. Think of it as your Mission Control. I’ve spent hours creating formulas, formatting cells, and tinkering with this template to align your distant company revenue goals with the Opportunities and MQLs you need to generate every month.
>> Related: How to Negotiate a Bigger Marketing Budget <<
How the funnel has shifted
Even if you hit your some goals, post-pandemic/stagflation funnel metrics have definitely shifted. We’re seeing:
- some campaigns surprisingly worked or underperformed
- trade shows and in-person events are still lightly attended
- a lot of teams are trying to dig out of a lead deficit
- win rates changed as people put purchases on hold or rushed to fill a gap
- pricing is dropping and sales cycles lengthening
- layoffs have limited what campaigns can even be executed
- annual revenue goals changed, with specific geographies or products newly prioritized
- marketing efforts are focusing on existing business
The path forward
Using a model, we want to validate what shifted and create new assumptions: What is realistic and achievable? Once we quantify the new reality, we can reallocate resources to the tactics that are still fruitful.
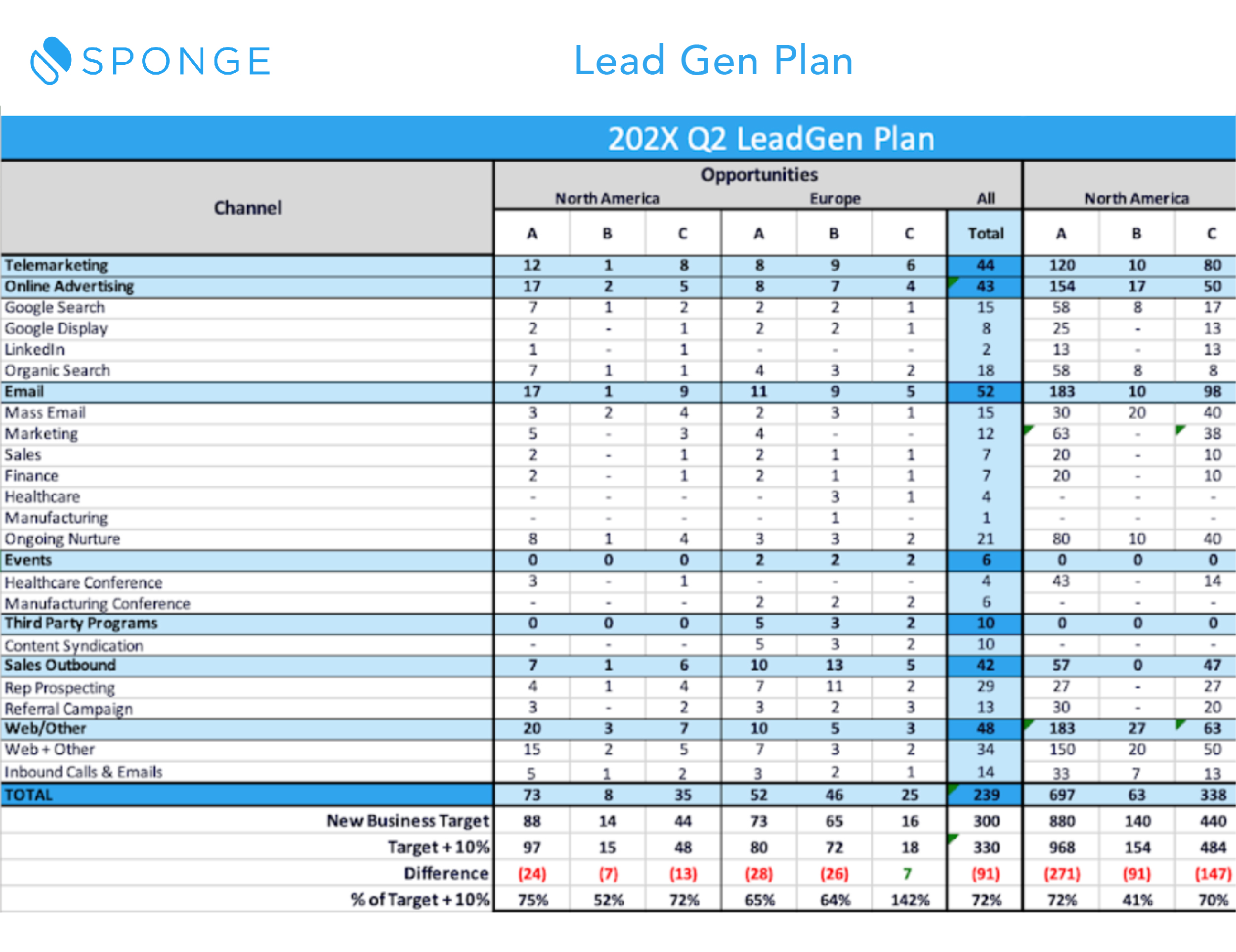
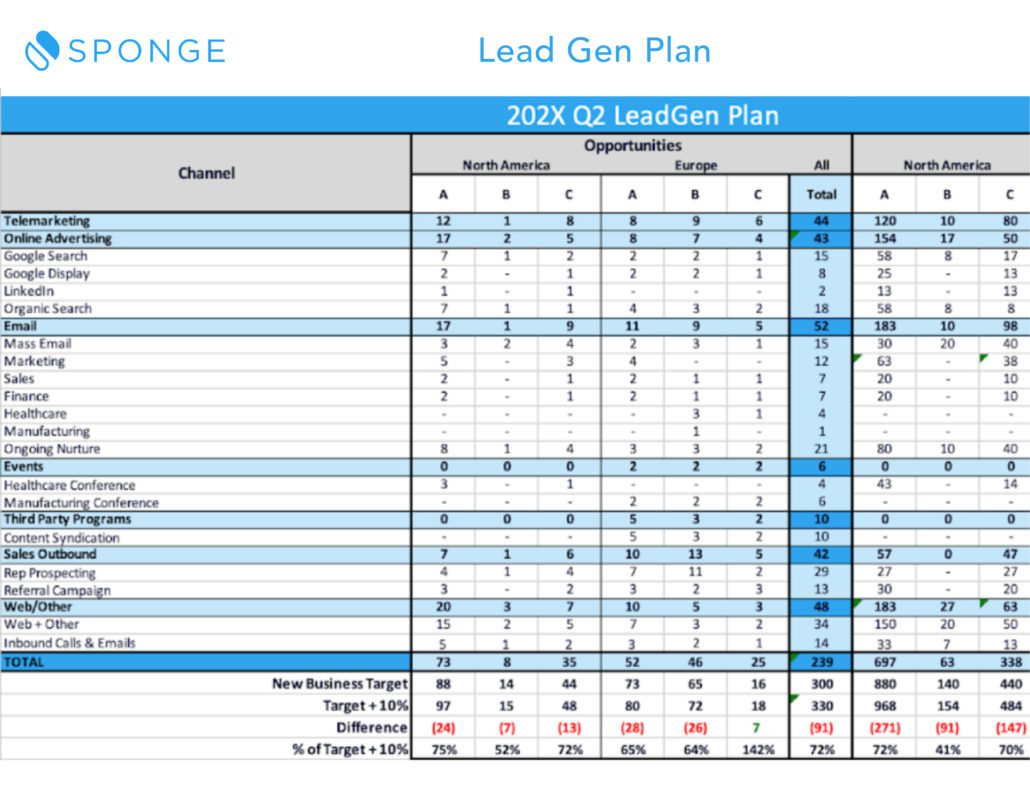
This template includes opportunity models for new and existing business (because the assumptions are likely different), and a lead gen plan. You plug in:
- your revenue goals
- sales capacity
- sales cycle
- ASP
- and funnel conversion rates
The model will do the rest and calculate how many Opps you need. And it will show you the cost of the leads and opps to get there.
Honestly, the first time you do this, you’ll probably have a CRAZY number of opportunities you need to generate, at a wildly out-of-budget cost.
That’s when you go back to your exec team, finance, and your sales leaders to say “Okay, if we want to get to these revenue numbers, in this environment, this is what needs to change.” An open conversation about poor assumptions helps lift the burden off marketing’s shoulders. And it’s a far more convincing negotiation when you’re armed with the model – rather than just suspecting the goals and budget aren’t achievable.
Video: column-by-column tutorial
In this workshop I go column by column through the entire demand gen model, helping explain how you can personalize it with multiple geographies and products.
FAQs
What is a demand gen model
A demand gen model refers to a strategic framework that organizations use to generate interest, awareness, and demand for their products or services. Demand generation is a comprehensive marketing strategy that aims to create and nurture leads throughout the entire sales funnel, from initial awareness to conversion.
How do I calculate revenue goals?
The process typically involves understanding the current business situation, considering growth objectives, and factoring in various components. You should do the following first before calculating:
- Review Historical Data
- Set Growth Targets
- Understand Market Conditions
- Segmentation and Product/Service Analysis
- Consider Sales Channels
- Factor in Price Changes
- Account for Seasonality
- Consider Operational Capacity
Regularly monitor your progress toward the revenue goals and be prepared to make adjustments if needed. If you find that your initial assumptions or conditions have changed, revisit and modify your goals accordingly.
Lastly, ensure that your revenue goals align with broader business objectives and strategies. This ensures that the pursuit of revenue growth supports the overall success and sustainability of the business.
What is sales capacity?
Sales capacity refers to the maximum level of sales activity and output that a sales team or individual salesperson can sustain over a specific period. It involves evaluating the resources, skills, and time available to the sales team and determining their ability to effectively engage with prospects, move leads through the sales funnel, and close deals. Understanding sales capacity is crucial for organizations to set realistic sales targets, allocate resources appropriately, and ensure that the team can meet or exceed its sales goals.
What is a sales cycle?
A sales cycle is the series of stages that a potential customer goes through before making a purchasing decision. A sales cycle may vary in length and complexity depending on the nature of the product or service being sold, the industry, and the specific sales approach of the organization.
What is ASP?
Average Selling Price (ASP) refers to the average price at which a particular product or service is sold over a specific period.
What is an opportunity?
An “opportunity” often refers to a potential sales or business deal. To make this less subjective, companies usually adopt a methodology for determining an opportunity, like BANT or MEDDPICC.