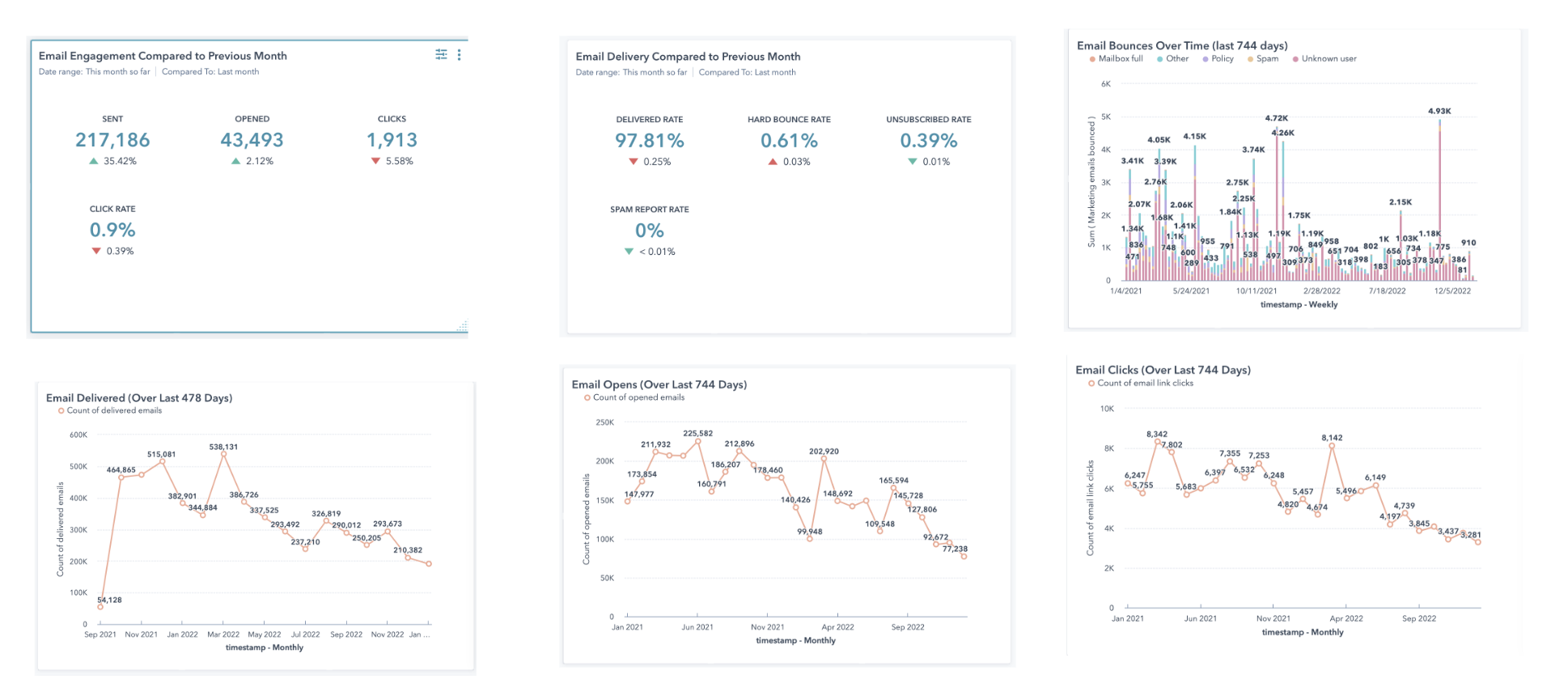
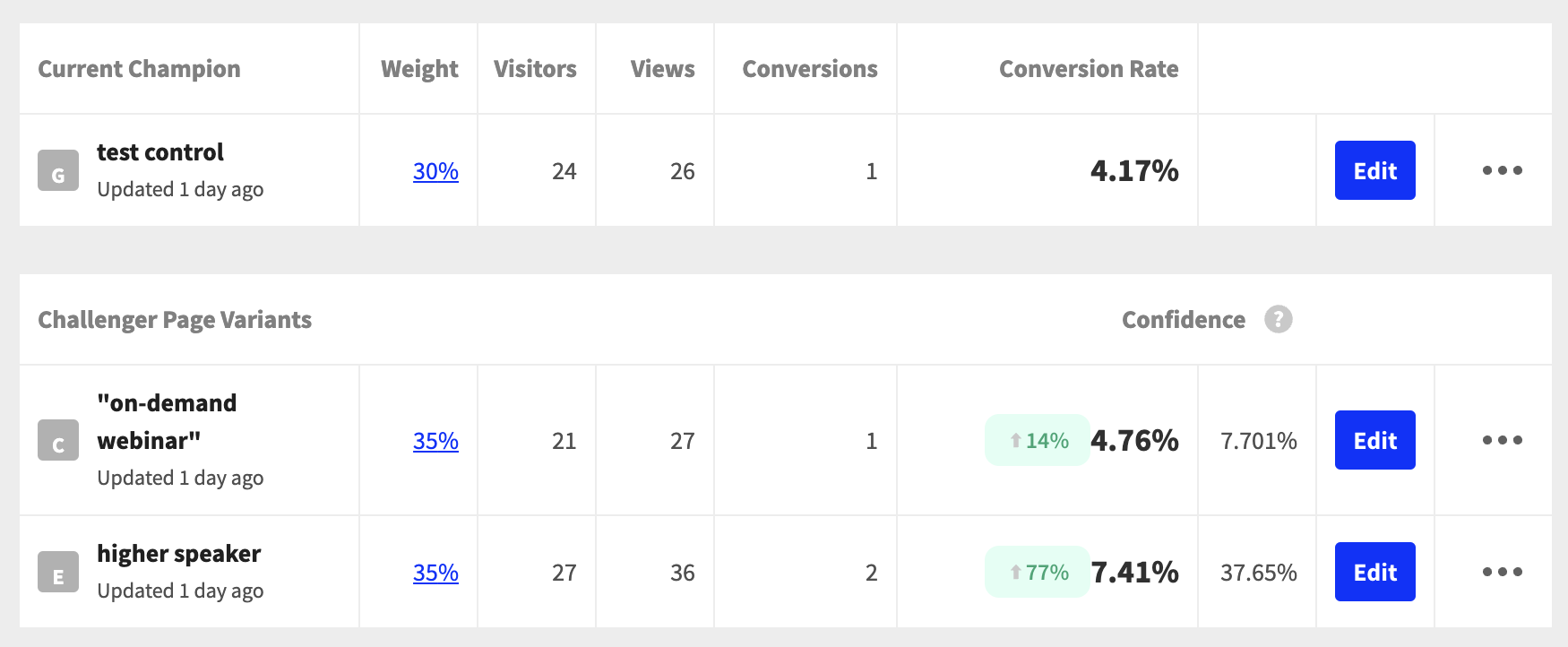
If you’re implementing HubSpot, one of the first steps is setting up your domains, SPF, and DKIM. Here’s how to set up HubSpot domains, SPF, and DKIM the first time around.
>> Related: How to Warm Up an IP <<
In this post:
First off, why are SPF and DKIM important in HubSpot?
SPF and DKIM are email security protocols that help ensure your emails aren’t flagged as spam. When you send 1:1 emails from your corporate email client, the SPF and DKIM are already configured by IT. And so your emails are rarely flagged as spam.
But when you send emails from HubSpot, they… come from HubSpot. Telling a spam filter “I’m an email from HubSpot on behalf of Acme Corp” looks shady. And it degrades your email deliverability rates and domain reputation.
So, by connecting your HubSpot instance to your company domain’s SPF and DKIM, your emails’ digital signatures are consistent and trustworthy.
Domain types in HubSpot
Firstly, it’s important to understand HubSpot’s different domain types.
- Brand domain: this is the same as your website domain (companyname.com)
- Primary domain: where certain content is hosted (blog.companyname.com, resources.companyname.com)
- Secondary domain: can be used for microsites/campaigns that are hosted separately from your main website (conference.companyname.com)
- Redirected domain: redirect traffic from any URL on a HubSpot-hosted domain
- Email sending domain: give HubSpot permission to send emails on your behalf, AKA DKIM (companyname.com, info.companyname.com)
Note: Review which ones are available to you based on the HubSpot subscription your organization is on.
Step 1. Give IT a heads up
Knowing you can’t send any emails (including IP warming) until this project is completed, give IT a heads up that this small project is coming.
Because the configuration process will require logging into your company’s DNS provider, you will need to schedule a call with the IT contact at your company.
We recommend scheduling a 60-minute meeting to explain why setting SPF/DKIM is important and what the process will look like. If you’re implementing for a small or newly-formed company, IT may need a little extra time to access their domain and email security records. We’ve definitely implemented HubSpot before a company even had IT headcount! Asking a part-time frontend web developer to sort this out in 24 hours is a recipe for failure.
Step 2. Decide what your subdomain(s) and email sending domain(s) will be
You will need to create separate primary domains based on the type of content you plan on promoting via HubSpot.
- The landing page primary domain will be the domain of all your HubSpot landing pages. It will be highly visible. We recommend using go, info, or discover.yourcompanydomain.com
- The email sending domain will be used for your HubSpot emails. This will also be visible to recipients. We recommend using companyname.com or info.companyname.com
Be sure to pick these naming conventions thoughtfully:
- Don’t use “marketing”, “hubspot”, etc. since those look spammy.
- Don’t use domains that are already used by IT! We want these to be unique to HubSpot so that ::knockswood:: if you’re ever blocklisted, your sales reps and accounts payable department and HR can still send 1:1 emails from the corporate email domain.
Step 3. Set up DKIM with IT
Note: IT will need to log in to HubSpot on their own machine. Be sure they have access to the platform ahead of the call.
Have IT log in to HubSpot and navigate to Settings > Website > Domains & URLs. During the call, you will provide the domains you selected for the company and walk them through the following steps depending on which domain type you are configuring:
For primary & secondary domains
- Click the “Connect to Domain” button, select Primary or Secondary, and select the hosted content type (Landing Page, Blog, Website, and Email).Choose your brand domain
- Specify where your content will be hosted
- Confirm your choices
- Login to your domain provider (GoDaddy, Cloudflare, etc.) and update the DNS records. HubSpot automatically provides the record type, host, and required data on this page.
- Click Verify. The hosting setup can take up to 80 minutes to complete, but you can check back to ensure it was configured successfully.
For redirected domains
- Click the “Connect to Domain” button, select Redirect
- Enter the domain you’d like to redirect first
- Then select the new domain you’d it to redirect to
- Login to your domain provider (GoDaddy, Cloudflare, etc.) and update the CNAME record. HubSpot automatically provides the record type, host, and required data on this page.
- Click Verify. The hosting setup can take up to 80 minutes to complete, but you can check back to ensure it was configured successfully.
And for email sending domains (DKIM)
- Click the “Connect to Domain” button, select Email Sending
- Enter the email address you will use to send marketing emails (ex. [email protected], [email protected], etc.)
- Login to your domain provider (GoDaddy, Cloudflare, etc.) and update the CNAME records. HubSpot automatically provides the record type, host, and required data on this page.
- Click Verify. The hosting setup can take up to 80 minutes to complete, but you can check back to ensure it was configured successfully.
Step 4. Set up SPF with IT
While SPF is not required in HubSpot (unless you’re using a DMARC policy), we highly recommend configuring it as it verifies the identity of the sender recipient email servers. To set up SPF:
- Have IT log in to HubSpot and the domain provider
- In HubSpot, navigate to Settings > Website > Domains & URLs
- Scroll to the bottom of the page and expand the Advanced Options section
- Click “Copy SPF Record” at the very bottom. It should look something like this:
- v=spf1 include:[Your HubSpot ID].spf [##].hubspotemail.net
- In the domain provider, update the SPF record.
FAQs
What is a spam filter?
A spam filter is a software or system designed to detect and filter out unsolicited and unwanted emails, commonly known as spam, from a user’s email inbox.
What is a DNS provider?
A DNS (Domain Name System) provider is a service that manages and operates Domain Name System servers. The DNS is a decentralized system that translates human-readable domain names, like www.example.com, into IP addresses that computers use to locate and connect to each other on the Internet.
What is an SPF?
SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework, and it is an email authentication protocol designed to help prevent email spoofing and phishing. SPF allows email senders to define which IP addresses are authorized to send emails on behalf of a specific domain.
What is a DKIM?
DKIM stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail, and it is an email authentication method designed to verify the authenticity of email messages. DKIM allows the sender of an email to digitally sign the message, providing a way for email recipients to confirm that the message was sent by an authorized sender and that it has not been altered in transit.
What is a subdomain?
A subdomain is a division or subset of a main domain. It allows for the organization and structuring of a website’s content in a hierarchical manner. Subdomains are created by adding a prefix to the main domain, creating a distinct web address that is still associated with the main domain.
What is a CNAME record?
A CNAME (Canonical Name) record is a type of DNS (Domain Name System) record that is used to map one domain name to another. In essence, a CNAME record serves as an alias for another domain, allowing one domain to resolve to the same IP address as the domain it is aliased to.